The Evolution and Basics of Electrical Discharge Machining (EDM)
The concept of EDM dates back to the late 18th century. Joseph Priestley, a pioneer in the field, noticed during his experiments that electrical discharges could erode material from electrodes, a phenomenon known as electro - discharge erosion. In the 1940s, Soviet physicist B. R. Lazarenko and American engineer Harold Stark independently developed the EDM process. However, it wasn't until the 1960s that commercial EDM machines emerged, sparking widespread industrial adoption. These early machines laid the groundwork for Wire Electrical Discharge Machining (Wire EDM) in the late 1960s and early 1970s, revolutionizing precision machining. Today, EDM is a staple in industries like aerospace, automotive, and medical manufacturing for creating complex shapes.
Understanding Wire EDM
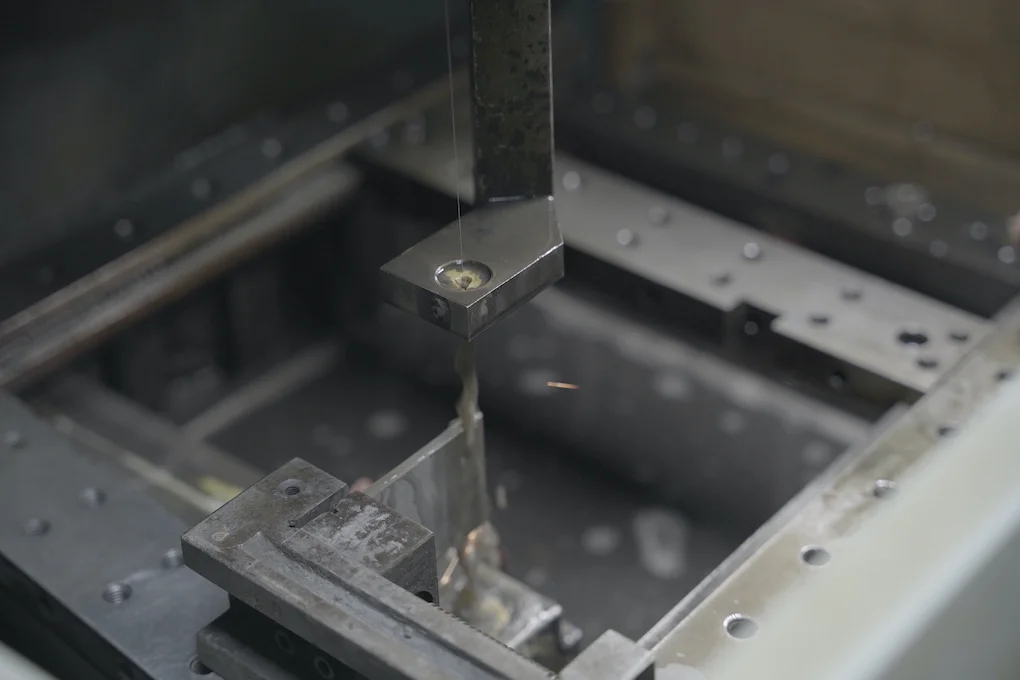

EDM is a precision machining process that relies on electrical discharges or sparks to remove material from a workpiece. It involves two electrodes: the tool - electrode (usually just called the tool or electrode) and the workpiece - electrode (the workpiece). High - voltage pulse currents between them generate sparks, melting and vaporizing the workpiece material. An adaptive control system regulates the electrode - workpiece gap to ensure consistent material removal, even with millions of discharges per second.
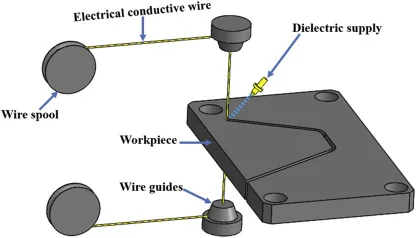
In Wire EDM, the two electrodes are a thin wire (usually brass or stratified copper, with diameters between 0.1 and 0.3 mm) and the workpiece. The wire, controlled by CNC, cuts the workpiece without any mechanical contact. In essence, Wire EDM is a non - contact subtractive manufacturing process. It uses a thin electrode wire and dielectric fluid to cut or shape conductive workpieces following a programmed path.
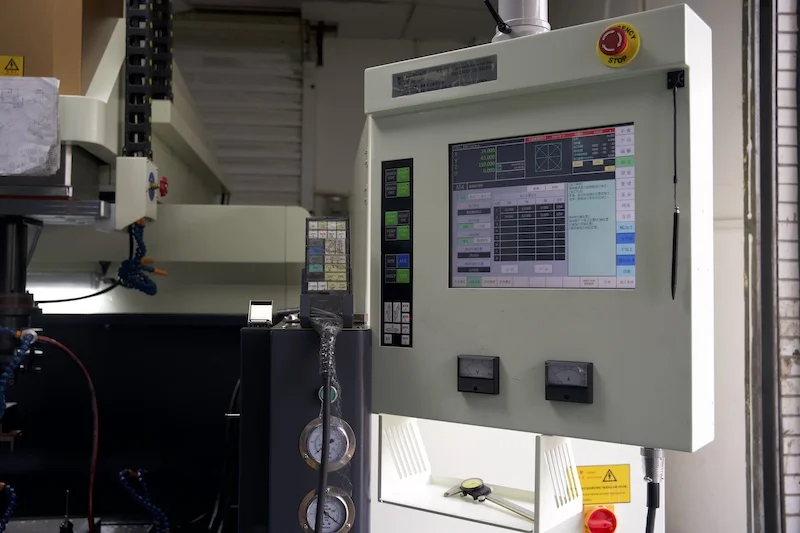

Types of Wires in EDM Machines
Brass Wires: Brass is the most popular choice in Wire EDM due to its good electrical conductivity and affordability. It's suitable for general EDM work, balancing cost and performance well.
Copper Wires: Copper wires are prized for their superior electrical conductivity, making them ideal for precision machining and high - speed cutting. But they come at a higher cost compared to brass.
Molybdenum and Tungsten Wires: These are used when extreme precision and thermal stability are required. Their high melting points and mechanical strength make them suitable for specialized applications, although they are more expensive.
Coated Wires: These are typically brass or copper core wires coated with materials like zinc or diffusion - annealed copper. The coating enhances conductivity and wear resistance, improving machining performance and extending the wire's lifespan. For example, zinc - coated wires can achieve better surface finishes and faster cutting speeds. Since wires degrade during the EDM process, they are disposable, and proper maintenance is crucial.
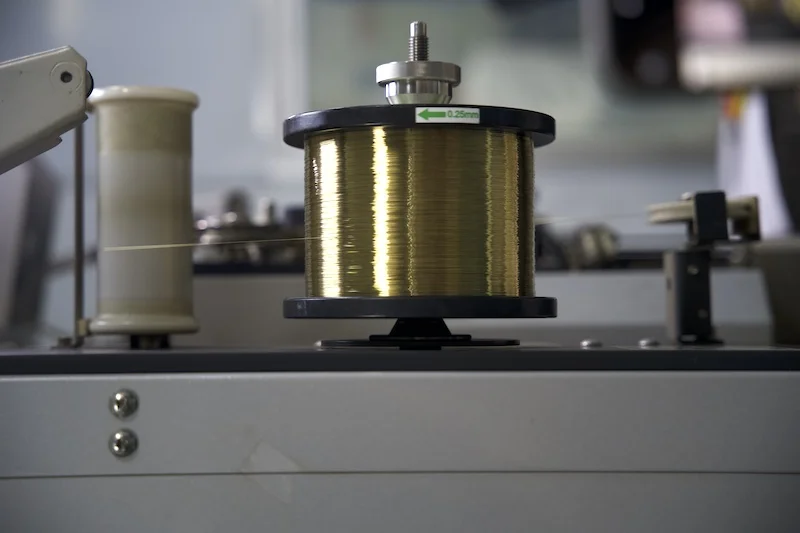

How Wire EDM Operates
Wire EDM is mainly used for cutting complex contours or cavities in hard, conductive materials. The wire and workpiece are submerged in a dielectric fluid (deionized water or oil). When the power supply charges the wire to the right voltage, a spark jumps between the wire and the workpiece, melting a small amount of material. You can start cutting either from a pre - drilled hole in the workpiece or from its edge. Each discharge creates a crater in the workpiece and affects the wire. By inclining the wire, parts with tapers or different top - and bottom - profiles can be made. The dielectric fluid cools the workpiece and wire, removes debris, and the process repeats until the desired shape is achieved.
Advantages of Wire EDM
High Precision: Wire EDM can achieve extremely high accuracy, often with positional precision in the range of a few microns. Specialized machines can reach accuracies as fine as 10 millionths of an inch (0.000001"). Cut parts usually maintain tolerances as tight as 0.0001", eliminating the need for additional finishing and leaving no burrs or distortion.
All - Metal Adaptability: It can machine conductive materials of varying hardness and brittleness, especially useful for heat - treated materials like pre - hardened die steels, titanium, stainless steels, tungsten, and molybdenum.
Low Distortion: As a non - contact process, Wire EDM minimizes mechanical stress, heating, and warping of the workpiece, making it perfect for delicate materials.
Shape and Angle Versatility: The wire can create complex geometries, tapered shapes, and sharp corners with small radii, and is suitable for machining small parts.
Processing Refinement: It excels at creating fine threads in hard materials, and is efficient for stacking, stringing, and nesting multiple parts.
Limitations of Wire EDM
Material Limitation: Only conductive materials can be machined, ruling out plastics, composites, and natural materials.
Slow Material Removal: Compared to processes like milling or turning, Wire EDM has a lower material removal rate.
High Costs: Wire EDM machines are expensive to buy and maintain. The disposable nature of the wires, along with other consumables, adds to the operating costs.
Applications of Wire EDM
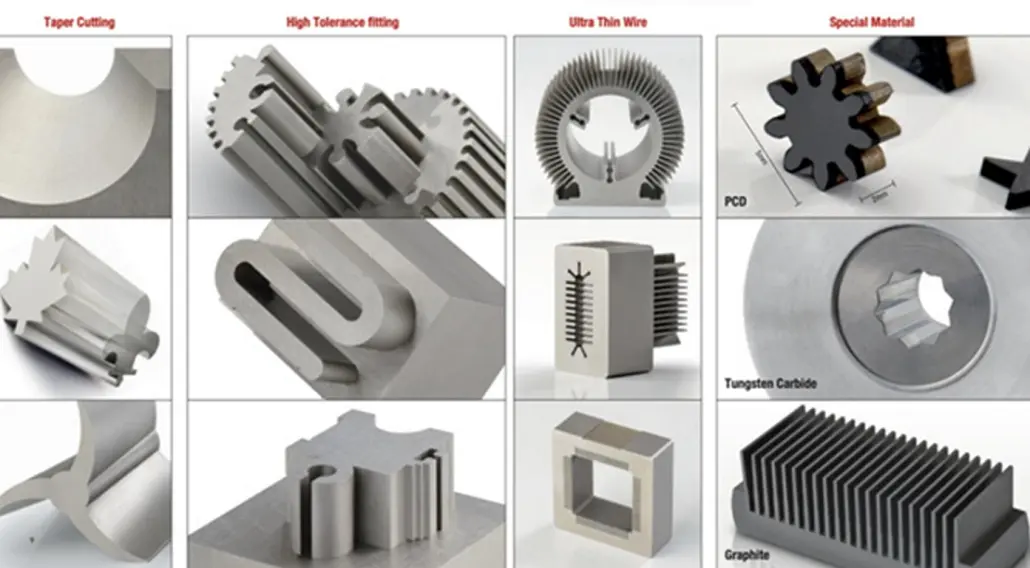

Tool and Die Making: Widely used in manufacturing molds, dies, and punches, Wire EDM's precision is essential for creating complex tooling components.
Aerospace: For machining aerospace components made from exotic alloys, Wire EDM ensures high precision, reliability, and consistency, especially for parts like turbine blades, nozzles, and engine components.
Medical: The medical industry benefits from Wire EDM's ability to produce small, intricate parts from hard materials like titanium and stainless steel, such as dental implants and surgical instruments.
Automotive: In the automotive sector, it's used for making precision components like gears, fuel injectors, and engine parts, especially for prototypes and small - batch specialized parts.
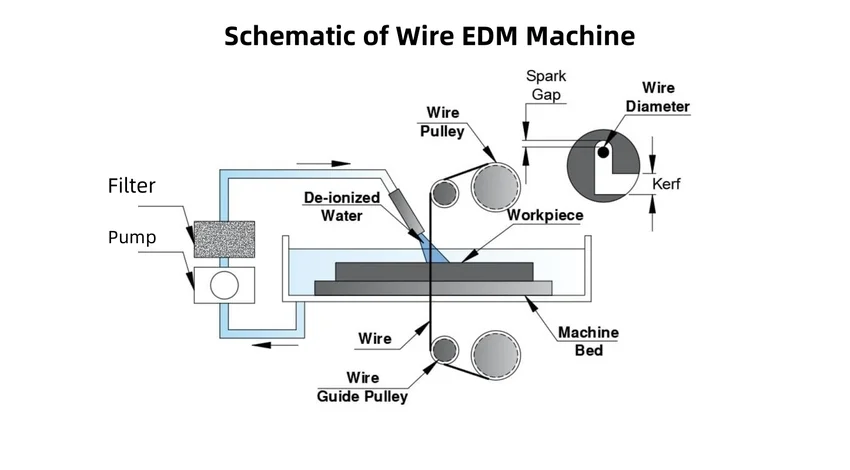
Components of a Wire EDM Machine
Worktable: Holds the workpiece and allows for precise multi - axis movement (usually X, Y, and Z axes) for cutting complex shapes.
Power Supply: Generates the electrical energy for spark discharges, controlling voltage, current, and pulse duration.
Wire: The thin metallic electrode, made of materials like brass, copper, or tungsten, through which electrical discharges occur.
Electrodes: In Wire EDM, the wire (cathode) and the workpiece (anode) act as the two electrodes.
Dielectric Medium: A dielectric fluid, like deionized water, flushes debris, maintains electrical discharge, and cools the workpiece and wire.
Control System: Comprising software and hardware, it enables operators to input parameters, control machine movements, and monitor the process.
Wire Guides and Tensioning System: Guides keep the wire straight and aligned, while the tensioning system prevents breakage and ensures consistent cutting.
Automatic Wire Threader: Some advanced machines have this feature to thread the wire through the workpiece automatically, saving time and reducing manual labor.
Filtration System: Removes contaminants from the dielectric fluid to keep it effective.
Frequently Asked Questions
Other Types of EDM: Besides Wire EDM, there's Sinker EDM (using a pre - shaped electrode like graphite or copper to create cavities in the workpiece, ideal for molds and complex 3D shapes) and Hole Drilling EDM (using a rotating tubular electrode for high - speed drilling of precise holes, like in turbine blades and fuel injection nozzles).
Difference between EDM and Wire Cut EDM: The main difference lies in the electrode. Wire cut EDM uses a continuous thin wire, enabling flexible and precise cutting of detailed contours. Sinker EDM uses a custom - shaped electrode, better for creating repetitive, deep, and intricate geometries in the workpiece.
Work with HL Parts for Your Wire EDM Projects
Until now, we have an overall understanding of wire EDM. Considering your projects, would it be suitable to be machined by wire EDM? Please don’t hesitate to contact us if you have any questions.
With over ten years of machining experience, HL Parts offers a wide range of manufacturing capabilities, including CNC machining and other value-added services for all of your prototyping and production needs. Contact us to request an instant quote!