Inch and Metric Standards of Drill Bit Size
This guide consolidates essential drill bit size information, including measurement methods, metric standards, imperial gauge systems, and their conversions. It serves as a reference for selecting appropriate drill bits across applications, with a focus on precision and compatibility.
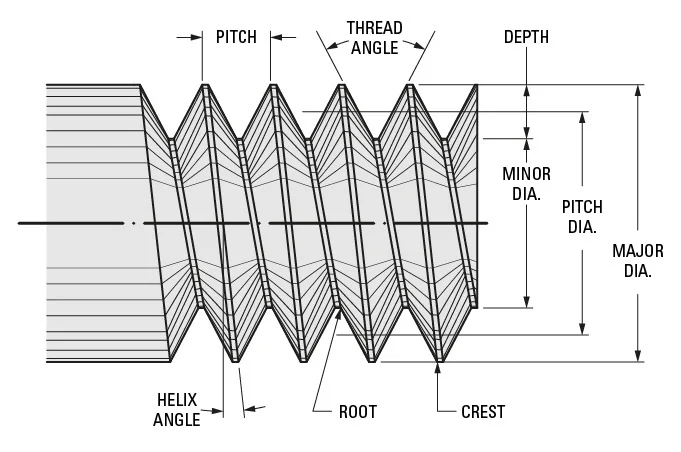
1. Drill Bit Measurement Methods
To accurately determine a drill bit’s diameter, measure the cutting edge (not the shank, which is clamped by the drill chuck). Use Vernier calipers for precision, noting that manufacturing tolerances typically range from ±0.005 to ±0.015 units (inches or millimeters), depending on bit quality.
2. Metric Drill Bit Sizes
Metric sizes are dominant in Europe and most global markets, defined by standardized increments. Key standards include:
2.1 British Standard (BS 328)
Applies specifically to twist drill bits, with diameters ranging from 0.2 mm to 25 mm. Sizing follows tiered increments based on diameter ranges:
| ø0.2 to 0.98 mm: | N. 0.1 mm N. 0.1 + 0.02 mm N. 0.1 + 0.05 mm N. 0.1 + 0.08 mm | N is an integer between 2 and 9 |
| ø1.0 to 2.95 mm: | N. 0.1 mm N. 0.1 + 0.05 mm | N is an integer between 10 and 29 |
| ø3.0 to 13.9 mm: | N. 0.1 mm | N is an integer between 30 and 139 |
| ø14.0 to 25.0 mm: | M. 1mm M. 1 + 0.25 mm M. 1 + 0.5 mm M. 1 + 0.75 m | M is an integer between 14 and 25 |
Note: Other bit types (e.g., Forstner bits) use non-BS 328 sizing.
2.2 Renard Series
A metric sizing system based on multiplicative factors, designed for standardized industrial use:
3. Imperial Gauge Systems (Number and Letter Gauges)
These gauges originated in the 19th century, loosely based on the Stubbs Steel Wire Gauge (with minor differences). They remain common in the U.S. and are occasionally used in the UK, but are obsolete in most of Europe. Sizes do not follow fixed mathematical increments.
| Gauge | inch | mm | Gauge | inch | mm | Gauge | inch | mm | ||
| 104 | 0.0031 | 0.079 | 52 | 0.0635 | 1.613 | A | 0.234 | 5.944 | ||
| 103 | 0.0035 | 0.089 | 51 | 0.067 | 1.702 | B | 0.238 | 6.045 | ||
| 102 | 0.0039 | 0.099 | 50 | 0.07 | 1.778 | C | 0.0242 | 6.147 | ||
| 101 | 0.0043 | 0.109 | 49 | 0.073 | 1.854 | D | 0.246 | 6.248 | ||
| 100 | 0.0047 | 0.119 | 48 | 0.076 | 1.93 | E | 0.25 | 6.35 | ||
| 99 | 0.0051 | 0.13 | 47 | 0.0785 | 1.994 | F | 0.257 | 6.528 | ||
| 98 | 0.0055 | 0.14 | 46 | 0.081 | 2.057 | G | 0.261 | 6.629 | ||
| 97 | 0.0059 | 0.15 | 45 | 0.082 | 2.083 | H | 0.266 | 6.756 | ||
| 96 | 0.0063 | 0.16 | 44 | 0.086 | 2.184 | I | 0.272 | 6.909 | ||
| 95 | 0.0067 | 0.17 | 43 | 0.089 | 2.261 | J | 0.277 | 7.036 | ||
| 94 | 0.0071 | 0.18 | 42 | 0.0935 | 2.375 | K | 0.281 | 7.137 | ||
| 93 | 0.0075 | 0.191 | 41 | 0.096 | 2.438 | L | 0.29 | 7.366 | ||
| 92 | 0.0079 | 0.201 | 40 | 0.098 | 2.489 | M | 0.295 | 7.493 | ||
| 91 | 0.0087 | 0.221 | 39 | 0.1015 | 2.578 | N | 0.316 | 8.026 | ||
| 90 | 0.0087 | 0.221 | 38 | 0.1015 | 2.578 | O | 0.323 | 8.204 | ||
| 89 | 0.0091 | 0.231 | 37 | 0.104 | 2.642 | P | 0.323 | 8.204 | ||
| 88 | 0.0095 | 0.241 | 36 | 0.1065 | 2.705 | Q | 0.332 | 8.433 | ||
| 87 | 0.01 | 0.254 | 35 | 0.11 | 2.794 | R | 0.339 | 8.611 | ||
| 86 | 0.0105 | 0.267 | 34 | 0.111 | 2.819 | S | 0.348 | 8.839 | ||
| 85 | 0.011 | 0.279 | 33 | 0.113 | 2.87 | T | 0.358 | 9.093 | ||
| 84 | 0.0115 | 0.292 | 32 | 0.116 | 2.946 | U | 0.368 | 9.347 | ||
| 83 | 0.012 | 0.305 | 31 | 0.12 | 3.048 | V | 0.377 | 9.576 | ||
| 82 | 0.0125 | 0.318 | 30 | 0.1285 | 3.264 | W | 0.386 | 9.804 | ||
| 81 | 0.013 | 0.33 | 29 | 0.136 | 3.454 | X | 0.397 | 10.08 | ||
| 80 | 0.0135 | 0.343 | 28 | 0.1405 | 3.569 | Y | 0.404 | 10.26 | ||
| 79 | 0.0145 | 0.368 | 27 | 0.144 | 3.658 | Z | 0.413 | 10.49 | ||
| 78 | 0.016 | 0.406 | 26 | 0.147 | 3.734 | R | 0.339 | 8.611 | ||
| 77 | 0.018 | 0.457 | 25 | 0.1495 | 3.797 | S | 0.348 | 8.839 | ||
| 76 | 0.02 | 0.508 | 24 | 0.152 | 3.861 | T | 0.358 | 9.093 | ||
| 75 | 0.021 | 0.533 | 23 | 0.154 | 3.912 | U | 0.368 | 9.347 | ||
| 74 | 0.0225 | 0.572 | 22 | 0.157 | 3.988 | V | 0.377 | 9.576 | ||
| 73 | 0.024 | 0.61 | 21 | 0.159 | 4.039 | |||||
| 72 | 0.025 | 0.635 | 20 | 0.161 | 4.089 | |||||
| 71 | 0.026 | 0.66 | 19 | 0.166 | 4.216 | |||||
| 70 | 0.028 | 0.711 | 18 | 0.1695 | 4.305 | |||||
| 69 | 0.0292 | 0.742 | 17 | 0.173 | 4.394 | |||||
| 68 | 0.031 | 0.787 | 16 | 0.177 | 4.496 | |||||
| 67 | 0.032 | 0.813 | 15 | 0.18 | 4.572 | |||||
| 66 | 0.031 | 0.787 | 14 | 0.182 | 4.623 | |||||
| 65 | 0.035 | 0.889 | 13 | 0.185 | 4.699 | |||||
| 64 | 0.036 | 0.914 | 12 | 0.189 | 4.801 | |||||
| 63 | 0.037 | 0.94 | 11 | 0.191 | 4.851 | |||||
| 62 | 0.038 | 0.965 | 10 | 0.1935 | 4.915 | |||||
| 61 | 0.039 | 0.991 | 9 | 0.196 | 4.978 | |||||
| 60 | 0.04 | 1.016 | 8 | 0.199 | 5.055 | |||||
| 59 | 0.041 | 1.041 | 7 | 0.201 | 5.105 | |||||
| 58 | 0.042 | 1.067 | 6 | 0.204 | 5.182 | |||||
| 57 | 0.043 | 1.092 | 5 | 0.2055 | 5.22 | |||||
| 56 | 0.0465 | 1.181 | 4 | 0.209 | 5.309 | |||||
| 55 | 0.0465 | 1.181 | 3 | 0.213 | 5.41 | |||||
| 54 | 0.055 | 1.397 | 2 | 0.221 | 5.613 | |||||
| 53 | 0.0595 | 1.511 | 1 | 0.225 | 5.791 |
Below is a standardized conversion table for number and letter gauges (inch to mm):
4. Key Notes
·Application Compatibility: Metric sizes are preferred for precision engineering (e.g., automotive, aerospace), while number/letter gauges remain common in U.S. woodworking, plumbing, and hobbyist projects.
·Standardization: Always verify sizing against project specifications, as non-twist bits (e.g., spade bits, hole saws) may follow alternative standards.
·Conversion Accuracy: Use the table above for direct inch-to-mm conversions, as gauge increments are non-linear and not mathematically derived.
Conclusion
At HL Parts, we specialize in providing top-quality mechanical machining services that are designed to meet your specific needs and help you stay ahead in a competitive market. Upload your file and let’s get started!